

IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium 2007
Istanbul, Turkey, June 13-15, 2007
Demo Day
Time: 10:00
Site: Istanbul Technical University Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Building, Inonu Cad. No: 87, Gumussuyu, Taksim
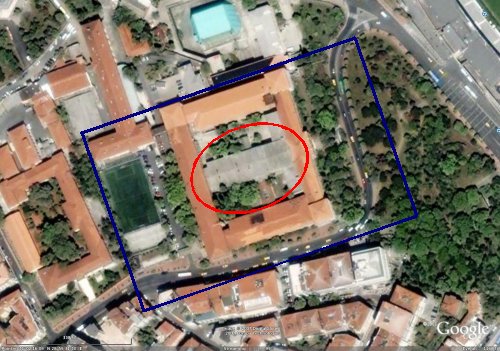
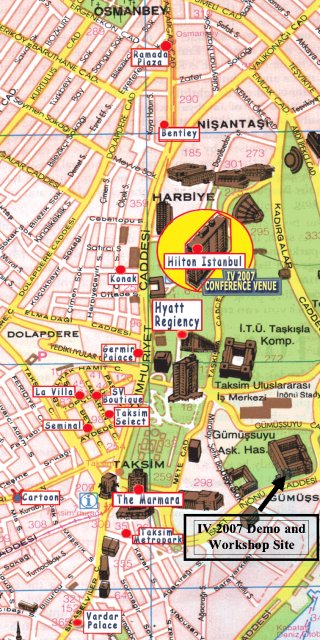
The 2007 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium demonstration day will take place at the Department of Mechanical Engineering of Istanbul Technical University. This is the city campus of Istanbul Technical University in Gumussuyu, Taksim and is within walking distance of all symposium hotels including the Hilton. A google earth picture of the demo day area and map of the site are shown below. Tea and coffee will be provided during the demo day.
Several different vehicles will be displayed during the demo day
- Aselsan İzci, an autonomous vehicle designed for patrolling borders.
- İTÜ Mekar Gezgin ITUnom, the autonomous vehicle of the Istanbul Technical University Mekar Labs and Autocom Center.
- Ford Otosan Fohev I, the second prototype of the Ford Otosan hybrid electric vehicle.
- Ford Otosan Active Chassis Control Vehicle.
- Aricopter, the İstanbul Technical University aerial robotics platform
DESCRIPTION OF DEMO DAY VEHICLES
Aselsan İzci


İZCİ is a concept demonstator of an unmanned ground vehicle developed by ASELSAN for remote operation of homeland security, asymmetric warfare, border surveillance, perimeter patrol, observation & reconnaissance missions. Autonomous behaviours of the vehicle are: waypoint navigation, path following, convoy following, obstacle detection & avoidance, and autonomous target detection&tracking.
Intempora RTMaps and SafeDriver

Imagined by professionals of the formation to answer risks of safety, behavior,economy and performance, SafeDriver is a modern tool at disposal of the listeners, trainers and learning wishing to take a lead in terms of pedagogy and technology. SafeDriver associates hardware and software allowing the recording and the visualization of the sessions of driving (image, sounds, speed, accelerations, braking...). In progress theoretical like in progress practice, the SafeDriver software allows the observation of the behavior of the drivers, for a safer drive.
The RTMaps software and “SafeDriver” system will be installed in a demo car and demonstrated. The system is made of a laptop, 4 webcams, 1 accelerometer, 1 GPS, and can be installed quite easily in a car provided there is a cigar-lighter plug available (to power the PC). It can acquire, display, record and playback these data in a synchronized manner.
İTÜ Mekar Gezgin ITUnom


This automous electric vehicle was converted from an electric golf cart. 2 new actuators were added to system to make it drive-by-wire. One of them is for steering and the other one is for braking. Traction power reference input was separated from the gas pedal and supplied directly to an electric motor controller. To measure wheel speed, an incremental encoder was located to motor shaft. To measure angular velocity and position of steering wheel, a steering angle sensor was located to the rack. Sonar sensors, laser scanner, camera and GPS receiver are being gradually added to the sensing system.
The electronic and computing hardware system includes a power unit,a1 signal conditioning unit and a rapid control prototyping hardware unit (Microautobox). The power unit is separated from the vehicle’s own power source and provides the necessary voltages for the auxiliary electrical devices. The signal conditioning unit is an interface circuit between the microautobox and the other devices. The main computations for operation and autonomy are taken care of within the microautobox. All logical operations are computed in this unit. Path generation, path following, automotic parallel parking and other algorithms are being realized in this laboratory type autonomous vehicle platform.
Ford Otosan Fohev I

FOHEV-1 is a light commercial vehicle, which is equipped with an internal combustion engine, a battery pack, an electrical machine and power electronics. Mechanical propulsion unit of the vehicle is hybridized with an electric propulsion unit. The electrical machine capable of transforming electrical energy into mechanical energy, or in the reverse direction, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy gives the advantages of implementing energy conversion on a real-time basis under the developed control algorithm. The controller reduces fuel consumption and undesired emission of internal combustion engine with the assistance of the electrical machine. Also, Regenerative Braking ability is used to recover the kinetic energy of the vehicle within the physical constraints of electric propulsion unit and regulation limits.
Ford Otosan Active Chassis Control Vehicle


Active Chassis Control project is a joint Project with İTÜ and FORD-OTOSAN. In the Project it is aimed to control the chassis movements of the light commercial Ford Transit Connect vehicle by semi active suspensions and active steering. Chassis motion in road vehicles are highly related to suspensions and steering oscillations. By using Continuous Variable dampers(CVD) in suspension system and controlled steering behaviour will provide improved comfort and vehicle dynamics whenever it is desired. The prototype vehicle equipped with 4 CVD, 8 acceleration sensors, a yaw rate sensor, a lateral acceleration sensor,a roll rate sensor and Dspace Control unit. The controller algorithms such as Skyhook, Groundhook or Hybrid controllers define a desired damping for the road conditions according to the driver’s commands. Therefore vehicle comfort and vehicle dynamics improved.
AriCopter : Aerobotics Flight Platform
ITU Control and Avionics Lab. (UUBF) and I.T.U. Mechatronics Lab. (MF)
ITU ROTAM


AriCopter is a COTS micro-helicopter heavily modified for research on tele-operation, real-time planning and embedded flight controls. The micro-avionics system embeds a multi-bus and distributed processor architecture. The current system allows video and flight information transmission and data-fusion across a wireless ad-hoc network.


The flight demonstration will show rapid deployment and plug-and-play networked operations in urban environments with aerial and ground equipment.
ARIba II


ITU Solar Car Team, founded in 2004, is a Project team made up of ITU students which have been participating in the Turkish Solar Challenge FORMULA-G. The team has created two solar cars so far; ARIba and ARIba II. The name is the combination of the symbol of ITU; bee “ARI” and the Turkish meaning of automobile “ARABA”. Recently ITU solar Car Team holds 9 titles and “Best Design Award” from the Turkish solar Challenge; FORMULA-G 2006 which was run in the Formula-1 Racetrack of Istanbul with the participation of 38 competent solar cars. Both being unique in design of many parts (Direct drive brushless DC motor and driver, vehicle body design, energy management system design and software, data acquisition system with CAN, RF communication…), the solar cars are powered by engineering of ITU.




